ISO 22000:2018 is a global standard that sets out the requirements for a Food Safety Management System (FSMS). Distributed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 22000 is relevant to organizations engaged with the established pecking order, counting food makers, processors, merchants, and providers. The standard gives a system for laying out, carrying out, keeping up with, and constantly working on a complete food safety framework.
ISO 22000 combines the standards of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points(HACCP) to distinguish, assess, and control food handling dangers.
The standard keeps the PDCA cycle, focusing on continuous improvement through arranging, executing, observing, and changing the food handling board system.
ISO 22000 promotes practical agreements through the established pecking order, ensuring that all applicable partners are educated about safety issues.
The standard includes necessities for carrying out major projects, like Good manufacturing practices (GMP) and disinfection methodology, to make an establishment for food security.
Organizations are expected to lay out frameworks for detectability and to promote strategies for the withdrawal of non-adjusting items to keep risky items from coming to purchasers.
ISO 22000 stresses the requirement for reported data to help the food handling the executive’s framework, including arrangements, techniques, and records.
Organizations are expected to lay out and keep up with a methodology for recognizing potential crises and answering them to ensure food handling.
The standard includes necessities for the approval of control steps, a check of the continuity of the food handling of the executive’s system, and nonstop improvement because of checking and assessment.
ISO 22000 combines the standards of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points(HACCP) to distinguish, assess, and control food handling dangers.
The standard keeps the PDCA cycle, focusing on continuous improvement through arranging, executing, observing, and changing the food handling board system.
ISO 22000 promotes practical agreements through the established pecking order, ensuring that all applicable partners are educated about safety issues.
The standard includes necessities for carrying out major projects, like Good manufacturing practices (GMP) and disinfection methodology, to make an establishment for food security.
Organizations are expected to lay out frameworks for detectability and to promote strategies for the withdrawal of non-adjusting items to keep risky items from coming to purchasers.
ISO 22000 stresses the requirement for reported data to help the food handling the executive’s framework, including arrangements, techniques, and records.
Organizations are expected to lay out and keep up with a methodology for recognizing potential crises and answering them to ensure food handling.
The standard includes necessities for the approval of control steps, a check of the continuity of the food handling of the executive’s system, and nonstop improvement because of checking and assessment.
The most common way of acquiring ISO 22000:2018 affirmation usually includes a few key stages:
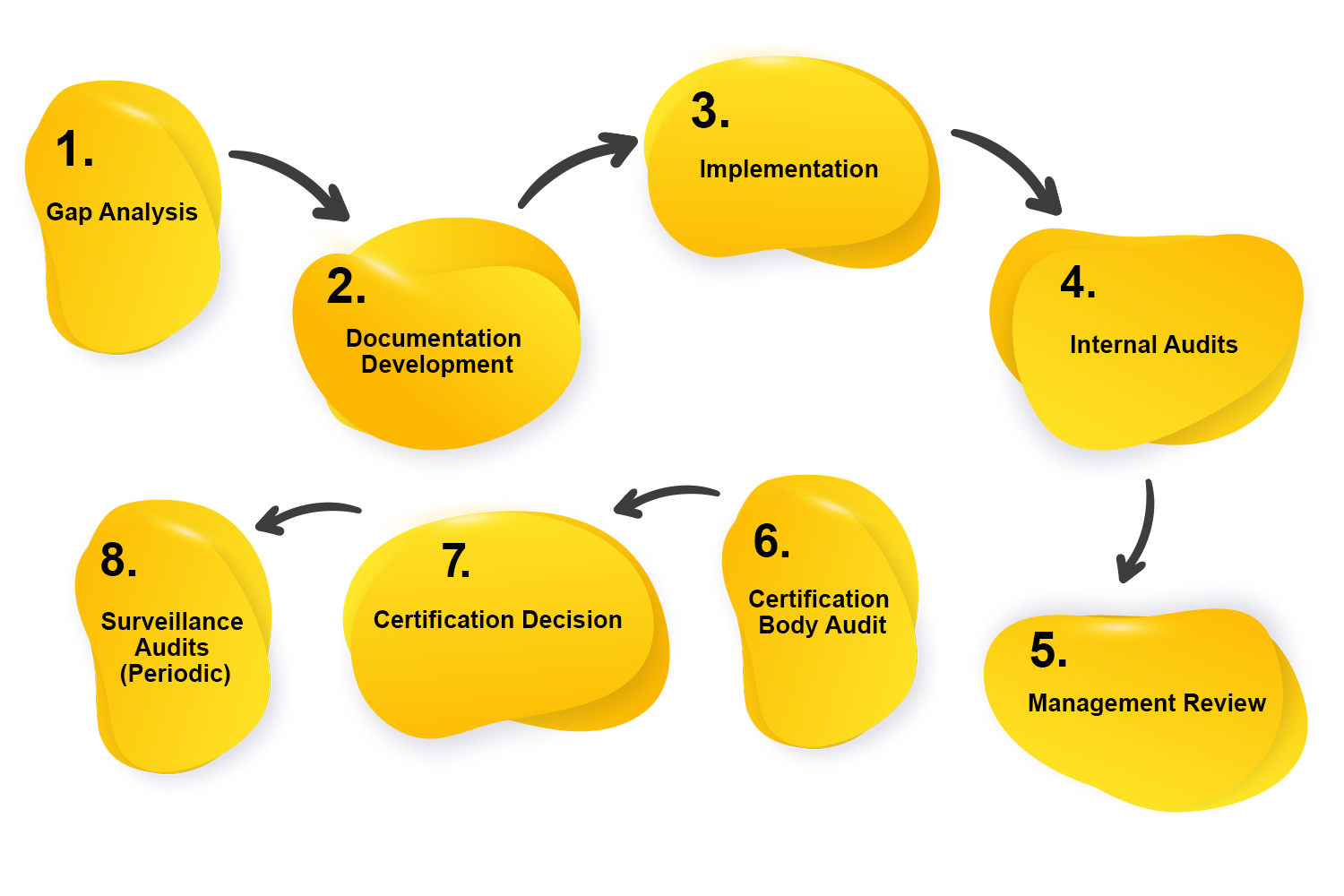
1. Gap Analysis: Analyze the ongoing safety of the board practices against the requirements of ISO 22000 to recognize gaps and areas for development.
2. Documentation Development: Create and execute important documentation, including the food handling manual, methodology, and records, to meet ISO 22000 requirements.
3. Implementation: Execute the safety executives’ framework all through the association, guaranteeing that every major cycle and control is set up.
4. Internal Audits:
Conduct an internal evaluation of the value of the implemented food safety management system and identify any issues or non-compliance.
5. Management Review: Prepare casual audits including top administration to evaluate the showing of the food security of the executive’s framework and plan for better.
6. Certification Body Audit: Hire an outsider certification body to review to evaluate consistency with ISO 22000 requirements.
7. Certification Decision: Check that the organization meets the requirements, the certification body gives an ISO 22000 declaration, showing consistency with the norm.
8. Surveillance Audits (Periodic): Go through occasional survey reviews by the certification body to ensure continuous regularity what’s more, constant improvement.
Legal4sure gaining practical experience in ISO 22000 Certification offers a scope of administrations to help organizations in the confirmation process. These administrations might include:
Do a careful complete review of the organization’s ongoing safety practices against the necessities of ISO 22000:2018. Find out the gaps and areas that need improvement to fulfill the guidelines.
Help create and implement necessary documents, including a Food Safety Manual, procedures, work instructions, and records, to meet ISO 22000 requirements.
Give direction and support during the execution of the safety board framework, guaranteeing that every single applicable cycle and control is set up.
Take the powerful execution of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) standards, which are essential to ISO 22000.
Guide the organization to picture out and execute major projects, for example, Good Manufacturing Product (GMP) and sanitization strategies.
Give present certificate support to help the association keep up with and continuously further develop its ISO 22000:2018 certification.
Help with directing inner reviews to assess the continuity of the carried out food security the board framework and recognize any non-similarities.
Offer help during the executive’s surveys, helping top administration with evaluating the execution of the safety board framework and plan for enhancements.
– Go about as a contact between the association and the certificate body.
– Help in planning for and organizing the outside review directed by the affirmation body.
Direct preparation projects to make the best among representatives about ISO 22000:2018 requirements and the importance of their jobs in guaranteeing food handling.
Guide the association in laying out successful correspondence processes and locking in important partners in the well-established pecking order.
Help with creating and carrying out techniques for crisis readiness and reaction to guarantee sanitation during any occasion.
Give procedures for continuous improvement because of observation, estimation, and assessment of the safety system.
Help with laying out and carrying out remedial and preventive activities to address distinguished non-similarities and prevent them from happening again.
An overall record that frames the association’s obligation to sanitation and gives an outline of the FSMS.
An assertion by top administration framing the association’s obligation to food handling also, meeting ISO 22000 necessities.
Recorded goals connected with food handling, lined up with the association’s by and large business goals.
Nitty gritty documentation framing the association’s HACCP plan, including peril examination, basic control focuses, and control measures.
Documentation of essential projects, for example, Great Assembling Practices (GMP), sterilization techniques, and different projects supporting the FSMS.
Reported techniques for key functional cycles that influence sanitation, including dealing with, handling, and appropriation.
Point by point headings for unequivocal and explicit undertakings and activities associated with hygiene, as expected by the FSMS.
Procedures for creating, reviewing, approving, and controlling documents and records related to the FSMS.
Methods for making, reviewing, supporting, and controlling reports and records associated and connected with the FSMS.
Strategies for organizing, coordinating, and detailing internal audits to study the sufficiency and adequacy of the FSMS.
Records of the board audits, including minutes of social affairs, what should be done, and decisions.
Records of educational and instructional meetings and health care events in relation with health and hygiene.
Frameworks for inside and outside correspondence concerning sanitation issues.
Documented and archived approach for recognizing and distinguishing potential emergency conditions and replying them to ensure health and hygiene.
Records of supplier assessments, endorsements, and consistent checking to ensure the security of moving towards materials.
Procedures and strategies for pulling out and auditing items if there should be an occurrence of security concerns.
Records connected with the observing and estimation of cycles, including gear alignment and Certification exercises.
Records of recognized non-similarities, remedial moves made, and check of their viability.
Records of interchanges connected with sanitation both inside the association and with outer partners.
Records of drives and moves made for the nonstop improvement of the FSMS.
























































































Your next step towards expert assistance is just a message away.
