Food Organic Certification NPOP/NOP USDA
Food Organic certification refers to the cycle by which farm items, including food things like fruits, veggies, etc. are checked to agree with organic farming standards. Two major organic certification standards are the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) in India (mainly caters the domestic areas) and the National Organic Program (NOP) under the US Division of Agribusiness (USDA). These certifications ensure that organic food items must follow the main concerns of farming, taking care of, and naming.
National Program For Organic Production (NPOP)
1. Country: India
2. Confirming Body: Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA)
3. Outline: NPOP is India’s public program for natural creation, managed by the Administration of Business and Industry. It spreads out the standards for natural development dealing with, taking care of, naming, and advancing natural things. APEDA is responsible for approving and controlling natural affirmation bodies.
National Organic Program (NOP) - USDA
1. Country: US
2. Guaranteeing Body: Different approve asserting trained professionals
3. Outline: NOP is the US government’s authority for organic farming managed by USDA. Natural certification showcases that things labeled as natural meet major rules related to soil quality, pest and weed control, and the use of added substances. Attesting experts authorized by the USDA complete the support circle.
Key Components Of Food Organic Certification
Organic Farming Practices
Organic Certification guidelines ordinarily expect to follow organic farming practices, which ban the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Soil
Management
Practices related to soil fruitfulness, treating the soil, and organic data sources are important. Organic certification often requires the execution of feasible soil the executive’s practices.
Crop Rotation and Diversity
Organic Certification cultivating focuses on crop rotation and variety to keep up with soil wellness, prevent irritations and sicknesses, and promote biodiversity.
Animal
Welfare
For products including animal farming (e.g., organic meat and dairy), certification rules involve important relations with the government’s assistance of creatures, including pasture and organic feed.
Prohibited
Substances
Organic Certification disallows the use of synthetic compounds, chemicals, anti-microbial, and certain added substances in organic production.
Record
Keeping
Complete record-keeping is required to follow the historical backdrop of every organic item from farm to market.
Inspections and
Audits
Regular observation and reviews by licensed specialists guarantee that farm and handling offices follow organic guidelines.
Labeling and Traceability
Check organic items should meet naming to accurately convey their organic status to customers. Detectability ensures the capacity to follow the origin of organic items.
Key Components of Food Organic Certification
Organic Farming Practices
Organic Certification guidelines ordinarily expect to follow organic farming practices, which ban the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Soil
Management
Practices related to soil fruitfulness, treating the soil, and organic data sources are important. Organic certification often requires the execution of feasible soil the executive’s practices.
Crop Rotation and Diversity
Organic Certification cultivating focuses on crop rotation and variety to keep up with soil wellness, prevent irritations and sicknesses, and promote biodiversity.
Animal
Welfare
For products including animal farming (e.g., organic meat and dairy), certification rules involve important relations with the government’s assistance of creatures, including pasture and organic feed.
Prohibited
Substances
Organic Certification disallows the use of synthetic compounds, chemicals, anti-microbial, and certain added substances in organic production.
Record
Keeping
Complete record-keeping is required to follow the historical backdrop of every organic item from farm to market.
Inspections and
Audits
Regular observation and reviews by licensed specialists guarantee that farm and handling offices follow organic guidelines.
Labeling and Traceability
Check organic items should meet naming to accurately convey their organic status to customers. Detectability ensures the capacity to follow the origin of organic items.
What Is Food Organic Certification NPOP/ NOP For Manufacturer, Re Packer & Trader?
The National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) and the National Organic Program (NOP) are organic certification norms relevant in India and the US, individually. These concepts give guidelines to the organic certification of different substances in the organic food production network, including makers, re-packers, and dealers. The standard that an association seeks will depend upon its area.
National Programme For Organic Production (NPOP) - India
Certification Process: Organic certification for makers includes agreeing with NPOP norms, which include organic farming works, handling, bundling, marking, and transportation. People should follow organic farming practices, use organic sources of info, and make sure that their handling offices maintain organic norms.
Certifying Body: Those who are looking for NPOP certification should be certified by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority(APEDA).
Certification Process: Re-packers dealing with organic items should keep NPOP rules for handling and bundling. They are needed to prevent the spoiling of organic items when dealing with bundling and naming.
Certifying Body: Re-packers should also look for certification from APEDA-certify certification bodies.
Certificate Process: Brokers must follow NPOP norms to gain organic certification during the exchange process. Brokers should ensure that the organic respectability of items is kept up with, and legitimate documentation is kept up with for discernibility.
Certifying Body: Like makers and re-packers, brokers should look for a certificate from APEDA-authorized certification bodies.
National Organic Program (NOP) - United States
Certification Process: Makers in the U.S. searching for NOP affirmation ought to adhere to Natural developing and taking care of standards shown by the USDA. The affirmation cycle incorporates showing consistency with NOP necessities, including using Natural trimmings and avoiding denied substances.
Certifying Body: Makers need to work with asserting experts affirmed by the USDA to achieve NOP affirmation.
Certification Process: NOP affirmation for re-packers incorporates ensuring that the repacking framework agrees to Natural standards. Re-packers ought to hinder the contamination of Natural things and stay aware of suitable documentation for detectability.
Certifying Body: Re-packers searching for NOP affirmation ought to work with avowing experts guaranteed by the USDA.
Certificate Process: Brokers associated with the taking care of and exchanging of Organic items should follow NOP guidelines to keep up with the Organic honesty of items. Appropriate documentation and record-keeping are fundamental for discernibility.
Certifying Body: Merchants looking for NOP certificates ought to draw in confirming specialists authorized by the USDA.
NPOP and NOP frameworks, the certification cycle includes a combination of on-location investigations, reviews, and observation of major standards for organic production. The certification plays a vital part in evaluating and ensuring elements inside the organic inventory network. Makers, re-packers, and dealers should follow the rules to keep up with the responsibility of organic items and give certification to shoppers.
What Is The Process To Attain Food organic Certification NPOP/NOP?
Achieving Food Organic Certification under the National Program for Organic Production (NPOP) in India or the National Organic Program (NOP) in the US includes a structured process. The certification is regularly overseen by certified certification bodies or offices perceived by the individual organic projects. The following is a general help for getting organic certification:
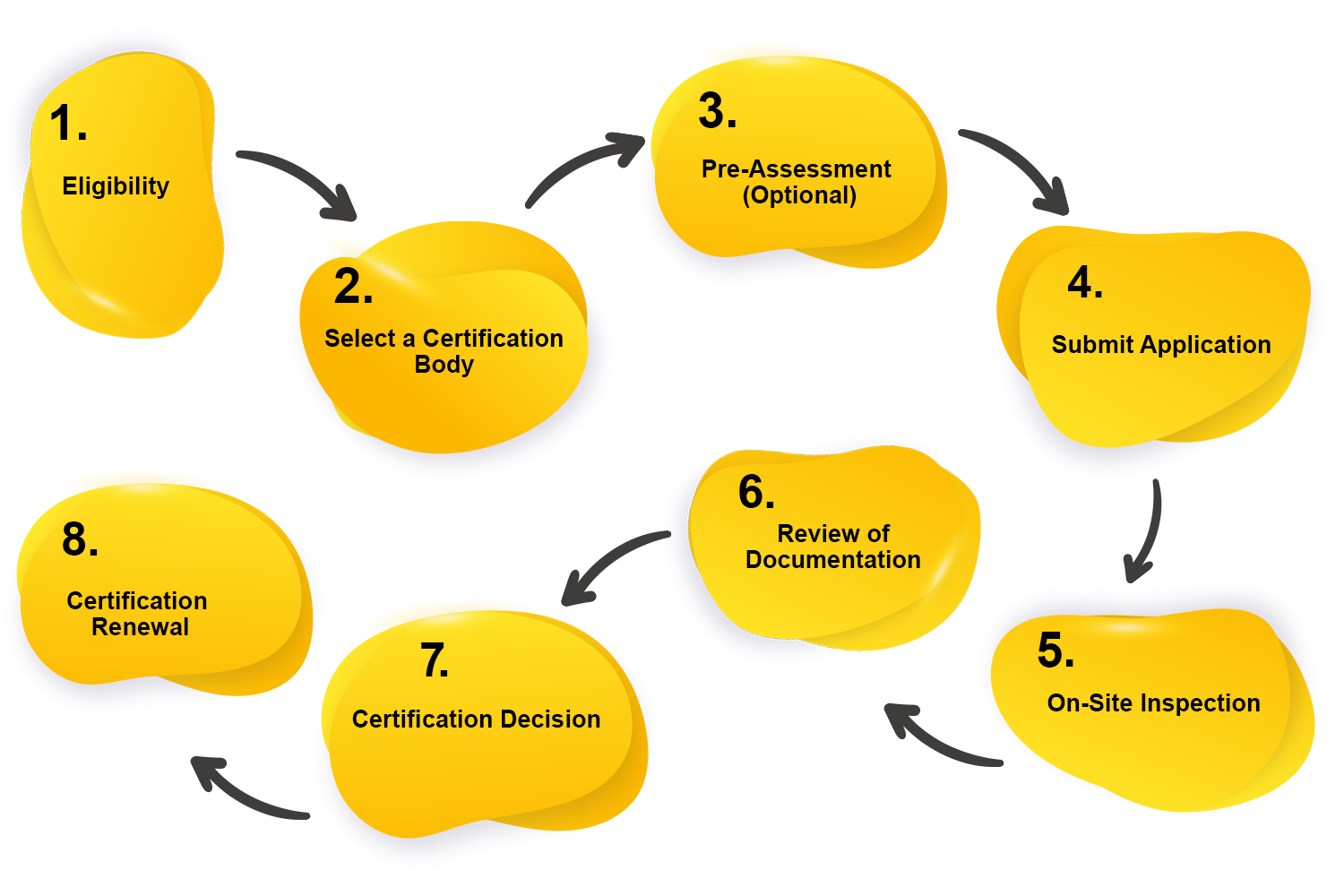
1. Eligibility: This ensures that your farming activity, handling unit, or exchanging exercises follow NPOP/NOP norms. Decide the particular certificate’s importance in light of your job as a farmer, processor, or broker.
2. Select a Certification Body: Select a certificate body certified by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA). The certification body will lead the evaluation and certification process.
3. Pre-Assessment (Optional): Consider going through a pre-evaluation by the certification body to find out the different areas of improvement.
4. Submit Application: Apply for organic certification to the picked certificate body. Involve all necessary documentation, like subtleties of the farm or handling unit, organic the board plan, and data on inputs used.
5. On-Site Inspection: The certification body will direct an on-location checking of your farm, handling unit, or exchanging premises. The review means to confirm consistency with organic guidelines.
6. Review of Documentation: The certificate body will audit the submitted documentation, including the organic executive’s plan and records. Guarantee that records show consistency with organic guidelines.
7. Certification Decision: The certification body will settle on a certificate choice in light of the on-location review and record survey. If agreeable, you will get an organic testament.
8. Certification Renewal: Organic Certification is normally applicable for a particular period. Restore your certificate through ordinary reviews and documentation refreshes.
Legal4sure Might Help In Achieving Food Organic Certification
Initial evaluation is a must for the client’s current practices to find out the gaps and areas where improvement or changes are required for maintaining organic standards. Provide a complete details report to meet certification requirements.
Helps in the improvement of an organic controls plan custom-made to the client’s particular activities.
Instruct the client in preparing them and coordinating the necessary documentation required for the certification application. Checking the major facts such as whether the records are finished, precise, and consistent with organic guidelines.
Help the client finish and present the certification application to the major certificate body. Guarantee that all expected data is remembered for the application.
Training and awareness programs are necessary. Direct preparation programs for client faculty to improve their knowledge of organic farming practices and require the certificate. Give direction on executing and keeping up with organic practices.
Prepare the client for the on-location investigation by the certification body. Host a pre-inspection scenario for acquiring the certification in reality.
Draft processes for continuous checking of organic consistency. Offer help with resolving the issues found during inspections.
Helps in checking the data is recent, guaranteeing that all documentation is up to date. Set up the client for reviews and investigations to keep up with certification.
Stay informed about changes in organic guidelines and principles. Encourage clients on the best way to adjust their practices to meet new requirements.
Act as a person of contact between the client and the certificate body. Address any questions or demands for extra data during the certification cycle.
List Of Document Used In Food Organic Certification Audit?
The documentation expected for a Food Organic Certification Review fluctuates depending upon the explicit Organic Certification program (e.g., NPOP, NOP) and the idea of the activity (e.g., ranch, processor, merchant).
Here is a general rundown of records ordinarily mentioned during Organic certification reviews
01
Organic Management Plan:
A far-reaching record illustrating the techniques and practices utilized to guarantee Organic trustworthiness in cultivating, handling, or exchanging activities.
02
Organic System Description
Definite data portraying the whole Organic framework, including Production techniques, handling systems, and taking care of practices.
03
Crop or Livestock Records
Records of yield turns, establishing timetables, and animals the executives rehearse showing consistency with Organic guidelines.
04
Field or Facility Maps
Maps demonstrating the format of the Organic Production regions, handling offices, or exchanging premises.
05
Input Records
Documentation of all data sources utilized in cultivating or handling, including manures, control substances, and revisions, with an emphasis on Organic endorsed inputs.
06
Record of Seed and Planting Stock
Data on the source and certification status of seeds, establishing stock, and domesticated animals.
07
Soil Management Records
Documentation of soil the board works on, including soil testing, revisions, and supplementing the board plans.
08
Water Management Plan
Subtleties of the water sources utilized in the activity and an arrangement for overseeing water quality.
09
Harvest and Yield Records
Records reporting reaped amounts, yields, and the attitude of Organic items.
10
Processing and Handling Records
Records of all handling and dealing with exercises, including gear cleaning, sterilization, also, isolation of Organic and non Organic items.
11
Product Labels and Packaging Records
Duplicates of item names and documentation connected with the bundling of Organic items.
12
Training Records
Documentation of preparing programs given to staff associated with Organic Production, handling, or taking care of.
13
Audit Trail Records
Records showing the detectability of Organic items from the source to the end result.
14
Complaint and Non-Conformance Records
Documentation of any protests and the remedial moves made because of rebelliousness issues.
15
Organic Certification Application
A duplicate of the underlying Organic certification application submitted to the certificate body.
16
Certificate of Compliance
The ongoing substantial Organic declaration was given by the certification body.
17
Renewal Application (if applicable)
Documentation submitted for the reestablishment of Organic Certification.
18
Communication with Certification Body
Any correspondence with the certification body, including notices of changes, refreshes, or then again demands for data.
19
Documentation of Regulatory Compliance
Evidence of consistence with nearby and public Organic guidelines, including any extra prerequisites well defined for the certification program.
Our Services














Our Services
















Our Associates & Certification Bodies















Our Associates & Certification Bodies















Our Clients














Our Clients